
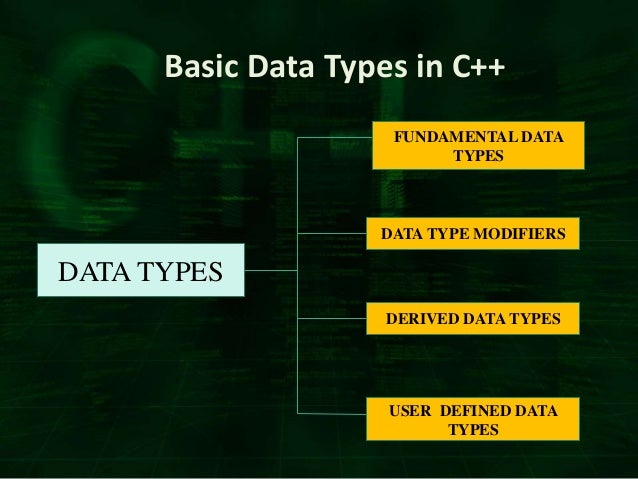
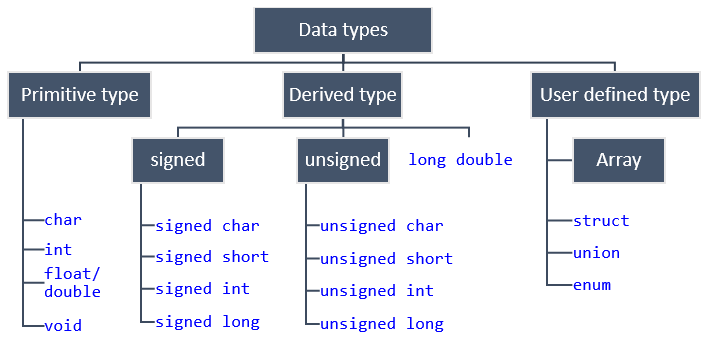
List of numbers, but it is different in that you can have both rowsĪnd columns of numbers. Primitive Data Types byte: The byte data type is an 8-bit signed twos complement integer. A matrix is like a vector in that it is a You must firstĬreate a matrix of numbers. To two-way tables (tables with more than one row). One-way tables (a table with one row), but it does not extend easily Possible to create the table directly, but the process is, If you know the number of occurrences for each factor then it is
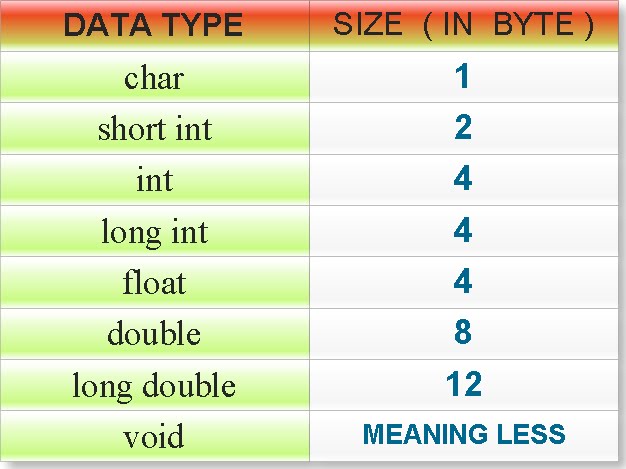
In the following example we convert tree$CĪ A B C 4 3 2 > attributes (results ) $dim 3 $dimnames $dimnames$a "A" "B" "C" $class "table" > summary (results ) Number of cases in table: 9 Number of factors: 1 This is a common problem and there is a way to tell R to treat the “C”Ĭolumn as a set of factors. This chapter provides an overview and more detailed description of the properties of the types in each category, and a summary of the data type storage requirements. These are factors and must assume that they are regular numbers. The data type of a programming element refers to what kind of data it can hold and how it stores that data. MySQL supports SQL data types in several categories: numeric types, date and time types, string (character and byte) types, spatial types, and the JSON data type. The researchers quite sensibly labeled these fourĮnvironments as 1, 2, 3, and 4. The basic strategy for selecting the best data type is to select the smallest data type that matches the kind of data you have and that allows for all the. Grown in an environment with one of four different possible levels ofĬarbon dioxide. ForĮxample, the first column, labeled “C,” is a factor. Go provides both signed and unsigned integer arithmetic. Researchers used numbers to indicate the different levels. Basic types (discussed in this chapter) include numbers, strings, and booleans. In this data set several of the columns are factors, but the When you use summary on a factor it does not print out theįive point summary, rather it prints out the possible values and the “CHBR” column are not all numbers R automatically assumes that it is aįactor. The discrete values cannot be subdivided into parts. Discrete data is a count that involves only integers. In statistics, marketing research, and data science, many decisions depend on whether the basic data is discrete or continuous. summary (tree $CHBR ) A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 3 1 1 3 1 3 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 1 3 1 1 C7 CL6 CL7 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 1 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 1īecause the set of options given in the data file corresponding to the As we mentioned above discrete and continuous data are the two key types of quantitative data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
